Please activate JavaScript in your browser to use all interface options.
 |
Carbon management in Rosneft: integrated approach to methane emissions reduction |


ROSNEFT CLIMATE GOALS SUMMARY
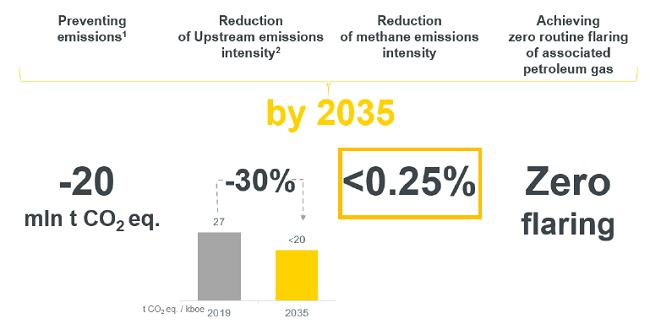
The Carbon Management Plan for the period until 2035 reviewed
by the Board of Directors on December 17, 2020
Note: All figures are for assets in Russia only.
1 Preventing of absolute Scope 1 and 2 (direct and indirect) emissions in comparable terms.
2 Scope 1 and 2 (direct and indirect) emissions.
In addition to the 2035 objectives, the Company will continue the search for additional opportunities to achieve net carbon neutrality by 2050.
 Rosneft designed a methane conversion facility producing synthetic liquid hydrocarbons. Тhe technology has received a number of expert reviews, including by the independent international consulting company Euro Petroleum Consultants, that characterized it as a high-technology modern solution. Rosneft is also developing methane aromatization technologies to produce both hydrogen and aromatic petroсhemicals from natural and associated petroleum gas.
Rosneft designed a methane conversion facility producing synthetic liquid hydrocarbons. Тhe technology has received a number of expert reviews, including by the independent international consulting company Euro Petroleum Consultants, that characterized it as a high-technology modern solution. Rosneft is also developing methane aromatization technologies to produce both hydrogen and aromatic petroсhemicals from natural and associated petroleum gas. 
Rosneft’s development strategy is aimed at achieving leading positions in application of the best available technologies, ensuring high profitability and maximum returns from the existing asset portfolio to the benefit of the Company’s shareholders and other stakeholders. Successful strategy implementation is based on minimization of the environmental footprint, effective carbon management, and reduction of the carbon footprint.
Reduction of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions is part of Rosneft-2022 Strategy that incorporates the Company’s commitment to the UN Sustainable Development Goals and contribution to implementation of the priority Climate Action goal.
In June 2019, Rosneft joined the initiative of leading international oil and gas companies and signed the “Guidelines for methane emissions reduction across the natural gas value chain” (hereinafter, “Guidelines for methane emissions reduction“). Eric Liron, Vice President for In-house Oilfield Services, signed the document on behalf of the Company. Eric Liron represents the Company on the Steering Committee of the Global Methane Initiative (GMI). In 2020, Eric Liron also took part in the annual round-table meeting “Guidelines for methane emissions reduction“ in London that was attended by business leaders from more than 20 of the world’s largest oil and gas companies.
Guidelines for methane emissions reduction were taken into account in the 2020 Carbon Management Plan and include the following:
- Sustainable methane emissions reduction;
- Improvement of performance (methane emissions control) across the value chain of gas business;
- Improvement of the accuracy of methane emissions data;
- Advancing the sound policy and legal and regulatory framework for methane emissions;
- Improving transparency.
In order to raise employee awareness of the main aspects of the carbon management, including methane emissions reduction, over 90 representatives of the management in the headquarters and regional divisions took part in 18 information sessions (distance participation).
METHANE EMISSIONS MANAGEMENT IS KEY TO COMBATTING CLIMATE CHANGE
Methane (CH4) is a hydrocarbon gas, a main component of the natural gas. The global warming potential of methane is estimated to be 28-36 times higher than that of carbon dioxide. For this reason, despite a relatively small volume of methane emissions compared to CO2 emissions, methane is the second greenhouse gas after CO2 in terms of its impact.*
The International Energy Agency estimates that the concentration of methane in the atmosphere is currently about 2.5 times pre-industrial levels and is increasing steadily. The most recent comprehensive estimate suggests that annual global methane emissions are about 570 mln tonnes.**

* Source: https://www.epa.gov/ghgemissions/understanding-global-warming-potentials
** Source: IEA, Methane Tracker 2020
Rosneft Group subsidiaries received Best Practice Guides for methane reduction with a view to assessing their practical use and applicability at the Company’s sites. The business planning process includes forecasting GHG emissions, action plans for detecting methane leaks (their quantitative evaluation), and actions aimed at reducing APG flaring and methane emissions.

MAIN SOURCES OF METHANE EMISSIONS
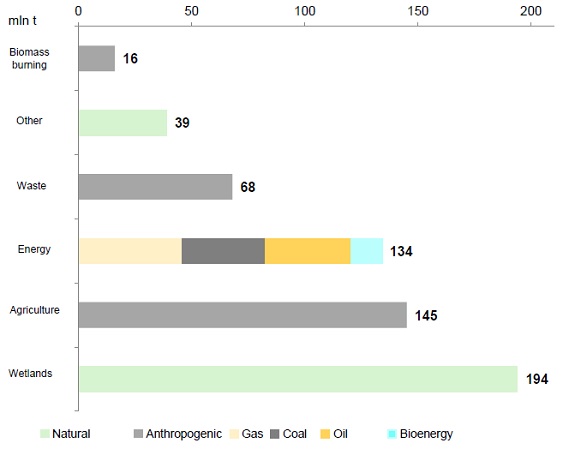
Source: IEA, Methane Tracker 2020
Energy resources – gas, coal, oil and biofuels (listed in the descending order) are second to agriculture (which accounts for about 25% of the total volume) in the anthropogenic sources of methane emissions.

MAIN SOURCES OF ANTHROPOGENIC METHANE EMISSIONS IN THE RUSSIAN OIL AND GAS INDUSTRY
Main sources of methane in the Russian Federation are determined in accordance with Order of the Ministry of Natural Resources and Ecology №300 dated 30.06.2015 “Оn Approval of Guidelines and Instruction for Quantitative Determination of the Volume of Greenhouse Gas Emissions by Organizations Conducting Business and Other Activity in the Russian Federation”, and in the oil and gas industry they include the following:
- Flaring of natural gas, associated petroleum gas and other hydrocarbon mixtures from blowdown of wells, the emptying and blowing-through of process equipment and pipelines, and from other process operations.
- Fugitive emissions include point-source emissions and emissions from non-defined places of CH4 and СО2 resulting from production, transportation, storage and processing of oil and natural gas.

The Company uses the national methodology for calculating the volume of methane emissions as a greenhouse gas specified in Order of the Ministry of Natural Resources № 300 dated 30.06.2015.

CALCULATION AND VERIFICATION OF METHANE EMISSIONS IN THE COMPANY
 Group Subsidiaries provide original information for calculating methane emissions, including flaring volumes of the hydrocarbon mix and its components, as well as information about the fugitive methane emissions.
Group Subsidiaries provide original information for calculating methane emissions, including flaring volumes of the hydrocarbon mix and its components, as well as information about the fugitive methane emissions.
HSE experts analyze the information provided by Group Subsidiaries, taking into account their core performance (commissioning new production facilities, construction of APG utilization facilities etc.), as well as looking at material deviations versus previous periods.
An independent external auditor verifies the processes of collecting, preparing, and consolidating methane emissions data.

APPROACHES AND TECHNOLOGIES APPLIED IN REDUCING METHANE EMISSIONS IN ROSNEFT. BENEFICIAL USE OF METHANE
In order to reduce emissions of hazardous substances resulting from APG flaring, the Company is implementing infrastructure projects for APG utilization in the following areas:
- Gas supplies to Gazprom’s unified gas supply system, as well as to own and third-party gas processing plants;
- Gas re-injection into reservoir;
- Gas utilization at generation facilities to generate electric power and heat;
- Gas utilization for own process needs in oil and gas treatment.
The Company carries out thermal treatment of gas at its upstream and downstream assets.

In 2013-2019, Rosneft’s capital investments in APG utilization projects amounted to RUB 147 bln.

SUCCESSFUL METHANE EMISSIONS REDUCTION IN 2019
The Company carries out actions aimed at reducing methane emissions and increasing the beneficial use of methane including flaring reduction and incremental efficiency in using hydrocarbons (own and process needs), detection of leaks at equipment and pipelines (involving daily inspections by personnel, and technical inspections by expert organizations). Also, the use of gas analyzer units with sound and light signals, and displaying gas contamination signals on the operator’s console, enables prompt response. In 2020, the Company continues to implement methane emissions reduction actions, and evaluates new opportunities for emissions reduction, including the use of advanced technologies.
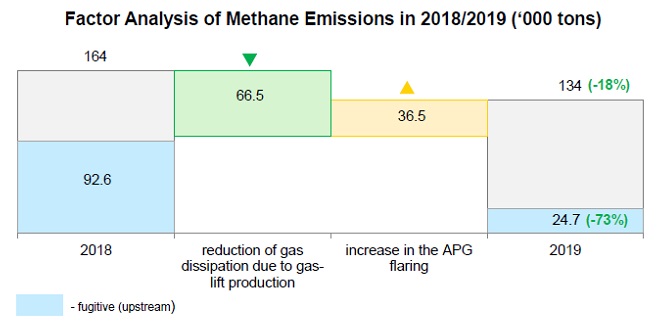
In 2019, the methane emissions reduction was mainly due to the commissioning of the system of oil and gas collection from wells to the group units and booster pumping stations at Troitskaya and Khankovskaya areas of Anastasievsko-Troitskoye Field, RN-Krasnodarneftegaz.
Perimeter: methane emissions indicators in the subsidiaries, which in accordance with IFRS are consolidated in proportion to their share, are shown based on 100% volume.

LLC KHARAMPURNEFTEGAZ - A SUCCESSFULL EXAMPLE OF REDUCING METHANE EMISSIONS
Kharampurneftegas is implementing a comprehensive approach to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, from optimized use of equipment and infrastructure to the application of advanced technologies, alternative sources of energy and elements of circular economy:
 Reducing APG flaring.
Reducing APG flaring.
High-pressure and low-pressure flaring facilities are the main sources of methane emissions in the subsidiary. In 2020, actions taken included re-activation and re-commissioning of small booster compressor stations, increasing the capacity of compressor units and increasing the throughput capacity of the field pipeline to the booster compressor station. Also, the manufacturer was engaged with a view to increasing the time interval between maintenance of gas engine compressors, thus, reducing the number of planned shut-downs of equipment, and the volumes of gas flaring.
LLC Kharampurneftegaz was established in February 2018 for development of the Kharampur field in the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Region in West Siberia, and is one of the most important projects for promoting the Company’s gas business.

Reducting methane leaks in the transportation system.
In 2021, the Company plans to use unmanned aerial systems (drones) for flying over Kharampurneftegaz fields on a daily basis for the purpose of methane leaks detection and prevention. The use of drones will improve efficiency and accuracy of identifying problems in low-temperature conditions of the Far North. The Company has successful experience of using drones in other subsidiaries, for example in Samotlorneftegaz and RN-Krasnodarneftegaz.

Continuous improvement of GHG emissions data accuracy.
High GHG emissions data accuracy in Kharampurneftegaz is ensured by:
- Taking stock of hydrocarbon blend composition at every field;
- Combining GHG emissions calculation based on the material balance and based on instrumental GHG emissions measurements;
- Taking into consideration all sources of GHG emissions including sources of emissions accounting for less than 5%;
- Ability to obtain data with the accuracy of less than 1 tonne of СО2 equivalent.
The project of the Kharampur field development is implemented in partnership with BP.
Proved hydrocarbon reserves amount to 3, 205.3 mln barrels of oil equivalent (PRMS).

The use of alternative sources of energy.
The main radio relay line of Kharampurneftegaz is fitted with alternative sources of energy – solar batteries generating electric power.

Separate collection and utilization of waste.
Since 2019, as part of introducing elements of circular economy in Kharampurneftegaz, the subsidiary has been implementing a system for separate collection and sending for recycling of plastic waste, paper, cardboard, glass, and waste scrap.
Employee awareness and involvement is key to successful implementation of the integrated approach to GHG emissions reduction in the challenging climate of the Far North. Educational seminars and training sessions in Kharampurneftegaz are aimed at improving the climate change awareness of the Subsidiary’s employees, and the understanding of contribution that can be made by every employee.
Green Office principles are being implemented at a rapid pace. The principles are aimed at the reduced consumption of resources, heat and electric power, improvement of working and environmental conditions.

METHANE EMISSIONS MONITORING
The testing showed a high efficiency of laser and thermal imaging devices for developing the system for timely detection and elimination of methane leaks contributing to greenhouse gas (methane) emissions reduction and improvement of safety conditions at the Company’s sites.
In accordance with the Methane Guiding Principles supported by the Company, the Leak Detection and Repair System is integrated into the current processes of equipment repair and maintenance.
In 2021, Rosneft plans to organize regular inspections of facilities in 10 core production subsidiaries for the purpose of methane leaks detection. The Company also intends to initiate a dedicated innovation project for developing a unified approach to the use of methane emissions reduction equipment.
Advanced technologies for methane leaks detection

The pilot testing program has been successfully implemented in three Rosneft Group subsidiaries – LLC RN-Krasnodarneftegaz, JSC Sibneftegaz, and JSC Samotlorneftegaz.

-315xx70.png)
 The Company
The Company